The NFS protocol uses ports 2049 and 111,2 and the Mac's built-in firewall blocks these by default. Open 'System Preferences, Sharing', and go to the 'Firewall' tab. You will see a list of network services that you can click on to enable or disable access - however, NFS is not on the list. Sounds like your 'lost' mounts are static, and can't be automounted again when Darwin occasionaly lets the NFS links go - dynamic mounts should solve this problem. Probably a good idea to just load your NFS info into NetInfo /mounts by hand (NI Manager), and not include that info in the /etc/fstab flat file.
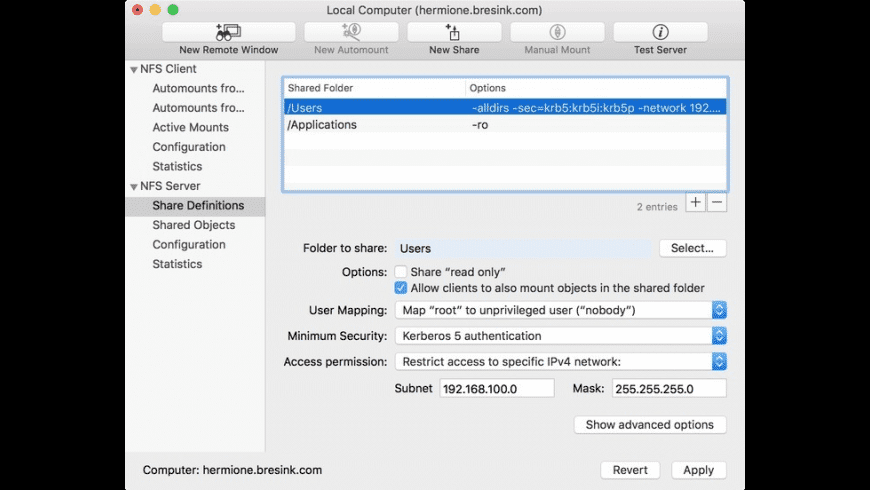
mount a file system
All files accessible in a Unix system are arranged in one big tree, the file hierarchy, rooted at /. These files can be spread out over several devices. The mount command serves to attach the file system found on some device to the big file tree.
The system maintains a list of currently mounted file systems. If no arguments are given to mount, this list is printed.
Mount Nfs Mac Os
The mount command calls the mount(2) system call to prepare and graft a special device or the remote node (rhost:path) on to the file system tree at the point node. If either special or node are not provided, the appropriate information is taken from the fstab(5) file.
“The Ten Commandments and the Sermon on the Mount contain my religion” ~ John Adams
Nfs Mount For Mac High Sierra
Related macOS commands:
bless - Set volume bootability and startup disk options.
diskutil - Disk utilities - Format, Verify, Repair.
df - Display free disk space.
hdiutil - manipulate disk images.
sharing - Create share points for afp, ftp and smb services.
umount - detach/unmount a device.
Nfs Mount For Mac Mojave
Some rights reserved

